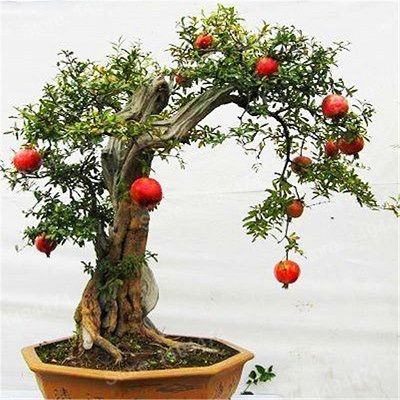
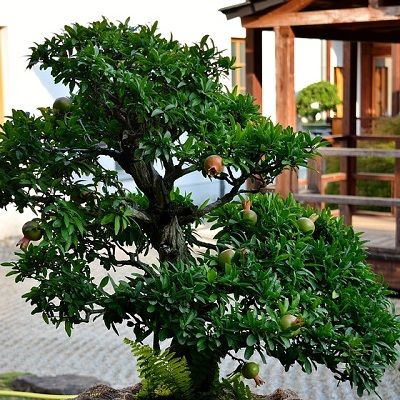
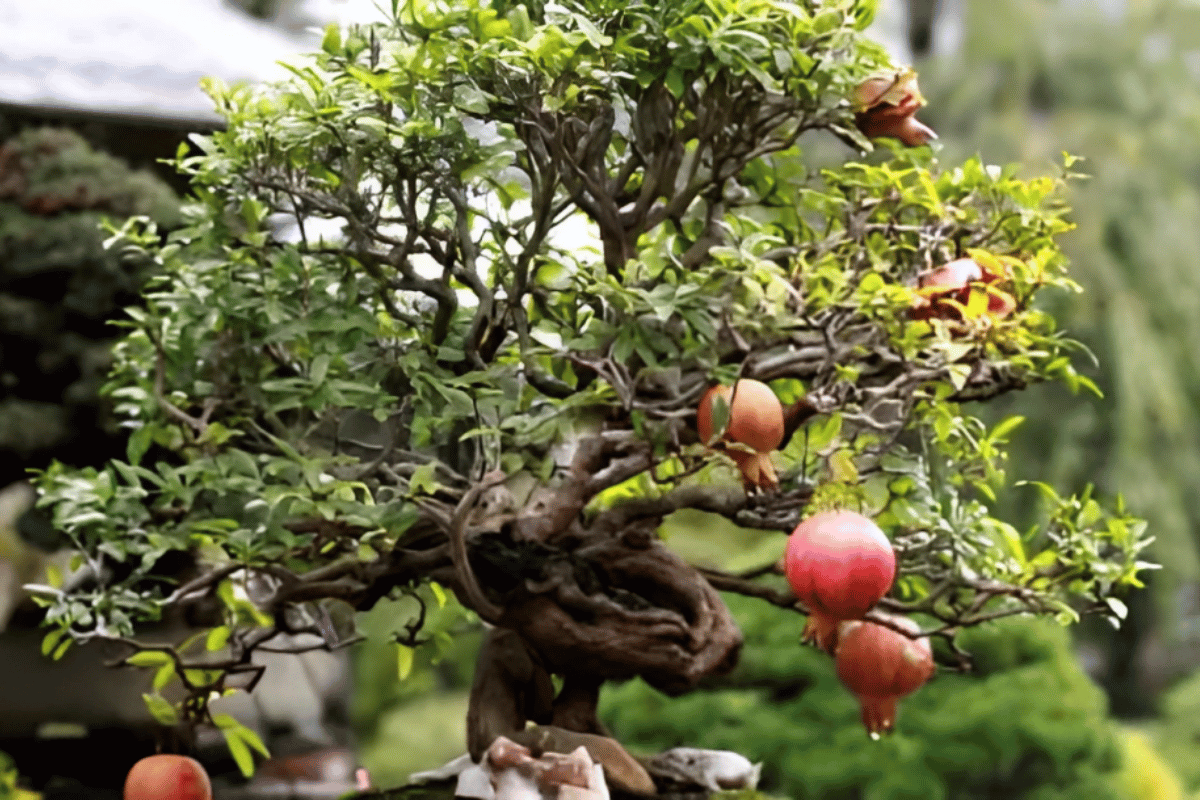
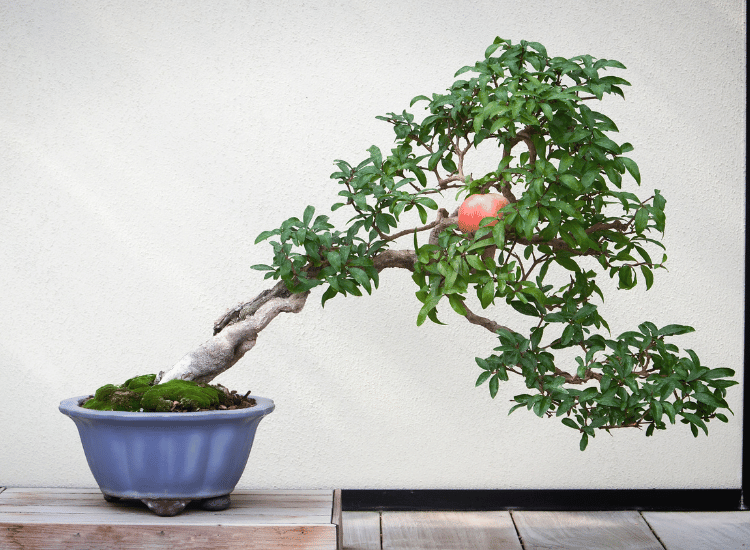
Bonsai cultivation is an art that offers a unique connection with nature, and the pomegranate bonsai, with its advantages and peculiarities, stands out as a great choice for cultivation.
Native to the Eastern Mediterranean and South Asia, this bonsai can be shaped in various styles.
Its brownish-gray bark that wrinkles and becomes scaly over time creates a unique and highly admired appearance in the world of bonsai.
In this article, you will learn a bit more about the characteristics and cultivation of this bonsai.
Characteristics and Curiosities of the Pomegranate Bonsai
Punica granatum is a tree that can grow up to 5 meters in height but is also commonly used as a bonsai.
The history of this bonsai begins in Japan and China, where the pomegranate was introduced through the silk road.
Over time, various cultures have attributed meanings to this plant; here are the most common ones:
- Passion
- Fertility
- Abundance
The technique of turning Punica granatum into a bonsai was first practiced in China and later made its way to Japan.
Its flowers and fruits have a red coloration that adds a special beauty to this plant. Its fruits, besides being beautiful, offer various health benefits.
Keep reading because below you’ll learn the step-by-step process to cultivate the pomegranate bonsai.
How to Care for the Pomegranate Bonsai
The pomegranate bonsai is a plant that has relatively simple care requirements.
In this section, you will learn from the beginning what care is needed to keep this plant healthy year-round.
To properly cultivate your pomegranate bonsai, you should follow the steps below:
- How to choose a pomegranate bonsai to cultivate
- Placement
- Watering
- Temperature and lighting
- Fertilization
- Pruning
- Transplanting
- Propagation
Mastering these 8 steps will make it much easier to keep your bonsais healthy.
Choosing a Pomegranate Bonsai to Cultivate
If you can visit a store to choose your bonsai, there are some characteristics of the pomegranate that can help you select a more beautiful and healthy plant.
- Trunk: It takes several years for the pomegranate to develop a thick trunk, and the trunk of a pomegranate is unlikely to thicken when cultivated as a bonsai. Therefore, look for a tree with a thick trunk.
- Bark: As mentioned at the beginning of this text, a wrinkled and scaly bark adds a unique beauty to this bonsai.
- Leaves and flowers: Look for healthy and vibrant leaves. If you visit the store during the flowering season of this plant, be cautious of faded, discolored, or spotted flowers.
- Cultivation history: Make sure that the place where you’re acquiring this plant is reliable and has bonsai experts. This way, you avoid the risk of buying a plant that may have pests or diseases.
After choosing your pomegranate bonsai, it’s time to learn the main care you should provide for it.
Placement
Thanks to its natural habitat’s climate, the pomegranate has an affinity for sunlight and can be cultivated outdoors.
The ideal condition for this bonsai is to provide 4 to 6 hours of sunlight daily. Therefore, a balcony or a well-lit window are great cultivation options.
During the hottest days, it’s advisable to prevent your pomegranate bonsai from receiving direct sunlight during the hottest parts of the day.
Similarly, be cautious of frost.
During winter, to ensure proper dormancy, aim to provide a temperature between 2°C to 8°C for your pomegranate bonsai, and always maintain good lighting.
Watering
Throughout the year, the watering needs of this bonsai change significantly.
Therefore, pay attention to the tips below to avoid mistakes in watering.
The first and most important tip is:
Water when the soil dries.
This will happen more often in summer when the pomegranate’s flowers appear. During this period, you might need to water twice a day.
In this case, water in the early morning and late afternoon. Watering your bonsai during the hottest times of the day can damage the roots and burn the leaves.
During winter, the frequency of watering will decrease significantly, sometimes requiring only twice a week.
During this period, be very cautious not to water when the temperature is too low, as this can freeze the soil and kill your plant.
Ideally, water your plant in the early morning.
Now, in spring and autumn, watering is usually done once a day. Try to water during the morning hours and avoid watering your plant during very hot or cold moments.
Checking If the Soil Is Moist
With the tips above, you’ll likely get the watering frequency of your pomegranate bonsai right.
However, there are several factors that can make your plant need more or less water, such as:
- Temperature: The higher it is, the more you’ll need to water
- Humidity: The higher it is, the less you’ll need to water
- Pot size: The larger it is, the less you’ll need to water (this can vary)
- Among various others.
Therefore, below you’ll learn how to check if the soil of your bonsai is moist. Remember that the ideal watering for the pomegranate is just after the soil dries.
Follow the 2 steps below:
- Insert your finger into the soil up to 2.5 cm (1 inch)
- Feel if the soil is moist.
During watering, be careful not to oversaturate your bonsai’s soil, as this can lead to diseases.
Temperature and Lighting
Lighting is likely the simplest factor in cultivating this bonsai.
Being a very resilient shrub that thrives on sunlight, the pomegranate bonsai should be placed outside your house or in a window with plenty of sun.
To provide adequate lighting for your mini pomegranate, follow the tips below:
- Direct sunlight in fall, winter, and spring, but ensure the substrate is moist.
- During summer, provide protection during the hottest hours (between 10:00 AM and 4:00 PM); typically, placing your bonsai on a balcony or under trees can be a good option.
Regarding temperature, the ideal range for this bonsai is 10°C to 25°C, while in winter, temperatures of 2°C to 8°C can support its dormancy.
Fertilization
Fertilization is extremely important for the development of your bonsais.
With it, you’ll be able to provide the nutrients your plant needs to grow, be healthy, and produce flowers and fruits.
For the pomegranate, there are two types of fertilization:
- Organic: Using natural fertilizers
- Inorganic: Using synthetic fertilizers
Normally, organic fertilization is recommended for cultivators who are still starting their journey.
This type of fertilization is milder, but it also poses lower risks to your bonsai.
To organically fertilize your pomegranate bonsai, follow the steps below:
- Use castor cake and bone meal
- Fertilize with just one of these every 2 months (e.g., month 1: castor cake – month 3: bone meal – month 5: castor cake, and so on)
Inorganic fertilizers require a bit more caution.
They are more efficient and faster, but you must be very careful not to over-fertilize your bonsai.
To avoid this mistake, we recommend using only half of the recommended dosage on the packaging.
For example, if the packaging recommends 20 ml per 1 liter, use 10 ml per 1 liter.
As for fertilization, follow these tips:
- Fertilize every 20 days
- Do not fertilize during winter or intense flowering periods
- To promote more flowers and fruits, use a fertilizer with higher phosphorus and potassium content from spring to summer (e.g., NPK 04 14 08)
- After repotting your bonsai, wait at least 3 months before the first fertilization
Choose the best fertilization method for you and fertilize your bonsai.
Pruning
Pruning is usually done in early spring, shortly after your tree bears fruits.
Known as maintenance pruning, this technique should be applied to prevent your tree from growing excessively.
To perform it, you should have a sharp pair of scissors to avoid “twisting” the branches of your pomegranate and causing damage.
Cut the branches that emerge from the undesired area of your bonsai.
NOTE: Triangular pruning is typically the best approach for the pomegranate bonsai.
Transplanting (Repot)
Repotting involves changing your bonsai’s pot.
This typically happens every 2 to 3 years, with younger plants requiring more frequent transplanting.
During transplanting, follow these tips:
- Clean the roots of your bonsai from the substrate
- Remove dead or rotten roots
- Avoid cutting thicker roots, as this can dry out some branches of your bonsai
- Transplant in spring
- After transplanting, place your bonsai in a location protected from the strongest sunlight
Propagation
Propagation is a slightly more advanced topic.
So, if you don’t want to propagate your bonsai, it won’t hinder your cultivation in any way.
Essentially, you can propagate your pomegranate bonsai through seeds or cuttings.
If you want to learn how to plant pomegranates, see this article.
And if you want to learn how to perform cuttings, watch the video below.
Cultivation from Seeds
Fortunately, pomegranate seeds sprout easily without much assistance.
Below are some tips that can increase your success rate in planting pomegranates.
- Plant during warmer months
- Clean and dry the seeds before planting
- Plant them in quality soil at a depth of about 1 to 1.5 cm (around 1/2 inch)
- Keep the soil moist and expose the pot to sunlight every day
- Wait for germination to occur; this can take up to 6 weeks
After a few months of cultivating your pomegranate, the first leaves will appear on your seedlings. At this point, you can transplant them into a pot.
Now, just keep caring for the plant and follow the steps in the video below to gradually transform your pomegranate tree into a pomegranate bonsai.
Remember that this is a lengthy process that can take years to achieve the ideal result of a beautiful bonsai.
So, be patient.
Conclusion
This was the complete guide on how you can care for your pomegranate bonsais without any difficulty.
If you want to learn about more bonsai species, check out the articles below:
- Jabuticaba Bonsai – Step by step to having fruits
- Orange Bonsai – How to Grow and Care Effortlessly
- Bamboo Bonsai – Care, Curiosities, and Main Species
And if you liked this article, leave your comments below and share it on your social media.