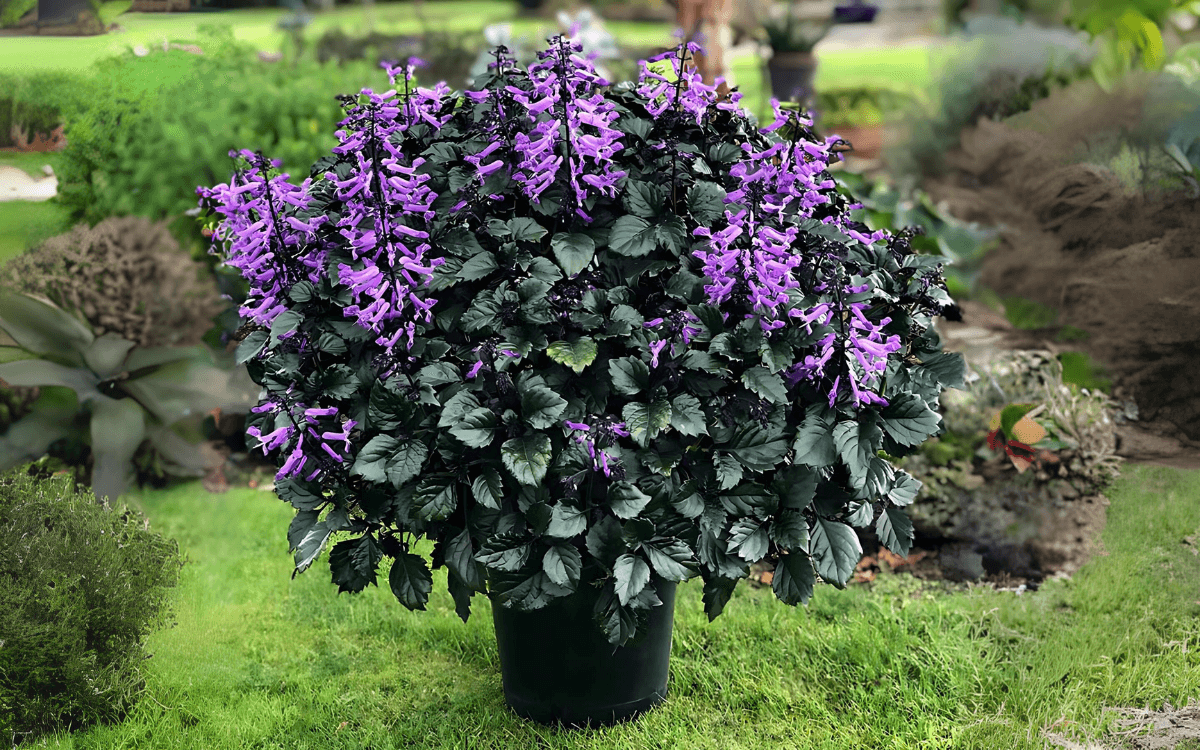
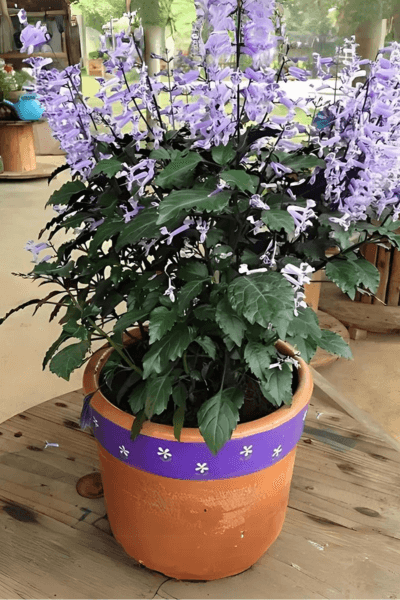
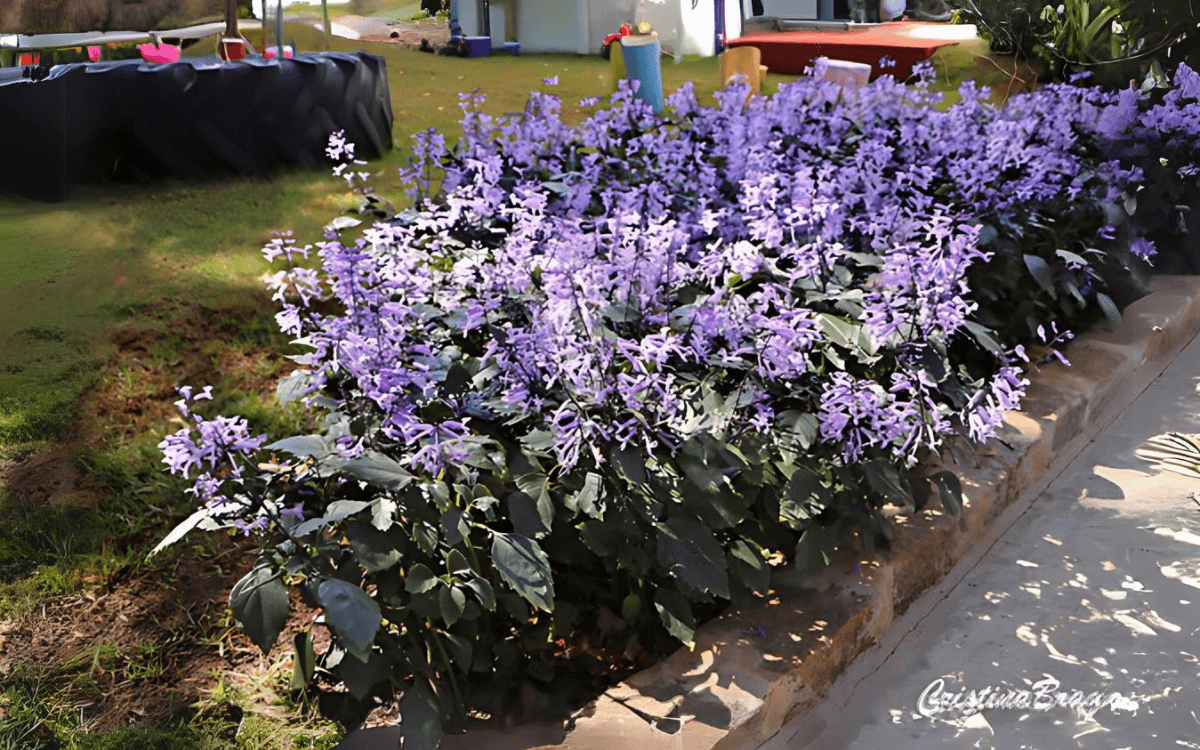
The Plectranthus saccatus, popularly known as stoep jacaranda has gained prominence for its beauty and ease of cultivation.
Native to South Africa, this plant belongs to the Lamiaceae family, the same as basil and mint.
With flowers especially in shades of lilac, white and purple that bloom throughout the year, Plectranthus saccatus attracts butterflies and hummingbirds, making it a great option for your garden or balcony.
Continue reading, because in this text you will learn about the characteristics, curiosities, and mainly how to care for and make the Plectranthus saccatus bloom.
Characteristics of the Plant
The leaves of the Plectranthus saccatus vary from dark green to light green, are rounded, aromatic, and can reach up to 6 centimeters (2.36 inches) in length.
One of the most admirable qualities of the Plectranthus saccatus is its ability to bloom throughout the year, offering a continuous display of flowers in shades of lilac, white, and purple. This perennial flowering cycle ensures that your garden or interior space is always vibrant and welcoming.
Considered an easy-care plant, the P. saccatus adapts well to both indoor and outdoor environments, resisting wind and requiring little maintenance.
Besides its beauty, the P. saccatus serves as a magnet for butterflies and hummingbirds, enriching your garden with the presence of these charming visitors.
See below for the care needed to keep this plant healthy and make it bloom.
Where to Plant
Thanks to its adaptability, the Plectranthus saccatus can be grown both indoors and outdoors.
When choosing a location inside the house, make sure the plant receives enough natural light and is protected from cold drafts.
In outdoor environments, it can be planted in flower beds or pots, providing a living and colorful decoration for balconies and gardens.
Ideal Soil
The base for the ideal soil starts with a rich composition in humus. Humus, resulting from the decomposition of organic matter, not only enriches the soil with essential nutrients but also improves its structure, increasing the water retention capacity while ensuring good drainage.
Incorporating organic compost or worm humus into the soil is a great way to achieve this desired richness.
The soil should also allow efficient drainage to prevent water accumulation at the roots, this can be achieved by ensuring that the soil is loose and not compacted, in addition to adding sand or perlite to improve permeability.
Read also:
- Ficus Pumila (Creeping Fig): How to Care and Propagate
- Tillandsia Air Plants: Species and Care (With Photos)
- Ribbon Fern or Cretan Brake Fern: How to Plant and Care
Correct Climate For the Plectranthus Saccatus
Although the Plectranthus saccatus needs a significant amount of sunlight to thrive, it is crucial to avoid direct exposure for prolonged periods, which can lead to burning of the leaves and flowers.
The ideal location combines full sun with partial shade, providing a few hours of direct sunlight daily, while protecting the plant during the hottest times of the day.
The P. saccatus prefers moderate temperatures, especially those that are not extremely hot. This preference makes it a perfect choice for gardens in regions with a temperate climate, where the seasons are well defined.
Another important care regarding the climate is to place your Plectranthus saccatus in locations with good ventilation, as this helps prevent pests and diseases.
How to Water
The Plectranthus saccatus requires regular watering to keep the soil consistently moist.
This means the soil should be checked frequently – preferably every day – to ensure it is slightly moist to the touch.
Watering should be done whenever the soil surface starts to dry, but before the entire soil becomes completely dry.
While the Plectranthus saccatus likes moisture, it does not tolerate waterlogged soil, which can lead to root problems such as rot. Therefore, ensure the soil has good drainage and that the pot or flower bed where the plant is cultivated allows excess water to drain.
When watering this plant, water directly the soil around the plant, avoiding wetting the leaves and flowers. This helps minimize the risk of fungal diseases, which can develop on wet foliage.
Fertilization
It is recommended to fertilize the Plectranthus saccatus every two months. This frequency ensures a continuous supply of nutrients, supporting the various growth stages of the plant, from leaf development to flowering.
Bone meal and wood ash are excellent organic fertilizers for the Plectranthus saccatus. They provide nutrients such as calcium and potassium, which are vital for plant development.
In addition, the application of an NPK fertilizer in the formulation 04-14-08 is recommended, as this specific combination of nutrients (low nitrogen content, high phosphorus, and moderate potassium) favors healthy flowering.
During the flowering season, the nutritional demand of the plant increases. At this time, it is recommended to intensify fertilization to every fifteen days, using the NPK fertilizer 4-14-8. Always water the plant before and after applying the fertilizer to minimize the risk of root burn and to facilitate nutrient absorption.
Pests, Diseases, and Other Problems
Water-soaked Spots: This disease is characterized by yellow spots on the leaves, which can significantly affect the growth of the plant. Prevention includes avoiding waterlogged soil and excessive moisture on the leaves. Make sure to water the plant at the base, keeping the leaves dry.
Root Rot: The occurrence of this disease is often associated with overly moist soil. The rotting of the roots prevents the plant from absorbing nutrients and water, leading to a general decline in health. Good drainage and moderate watering are essential to prevent this condition.
Aphids, Thrips, and Mites: These pests feed on the sap of the plant, weakening it. Aphids and thrips can also transmit viruses from one plant to another. Control can be achieved through the application of specific insecticides or natural solutions.
Discoloration of Flowers: The loss of vibrancy in the colors of the flowers can be a sign of lack of sunlight or inadequate fertilization.
Leaf Drop: Both excess and lack of water can cause leaf drop.
Additional Tips
Below I have separated some additional tips for cultivating the Plectranthus saccatus that were not mentioned above.
- Choice of Pot: choose one that has holes in the bottom to allow adequate drainage.
- Strategic Location: if cultivated indoors, an east or west-facing window is ideal, as it offers perfect filtered sunlight for the plant.
- Acclimatization: If you bring a new P. saccatus plant home, or if you move it from inside to outside (or vice versa), do it gradually to allow it to adjust to the new light, temperature, and humidity conditions.
- Protection During Winter: in regions with cold winters, protect your P. saccatus from extreme cold. If it is in a pot, move it inside the house or to a protected location. If it is planted in the garden, consider covering it to help insulate the soil.
- Other uses: a study pointed out the use of a substance taken from Plectranthus saccatus to combat the insect Spodoptera littoralis. Regarding its medicinal properties, a study demonstrated that the extract of this plant may present a new alternative for the treatment of gout.
Below I have separated some texts that I wrote about other plants that can also be cultivated in your home or garden, I believe they may interest you.
- African Iris: How to Care and Propagate
- Sandpaper Vine (Petrea volubilis): Care and Propagation
- China Rose (Rosa chinensis): 8-Step Care Guide
- Japanese Fern Tree – How to Care and Characteristics
Also, share this article on your social networks and leave a comment below.















