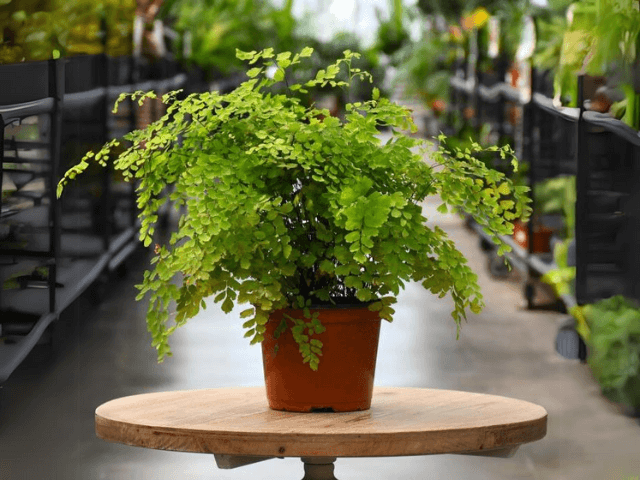
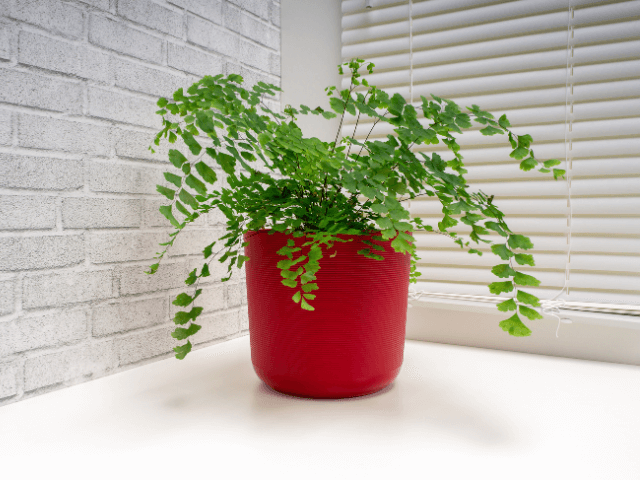
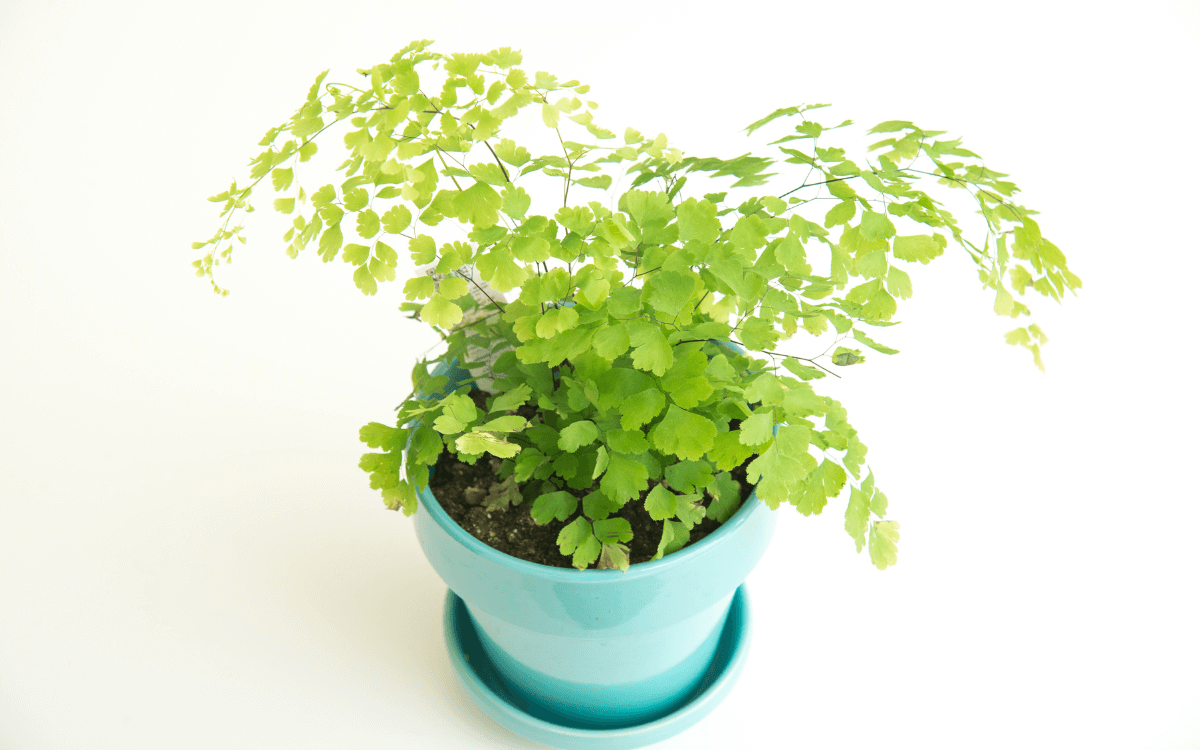
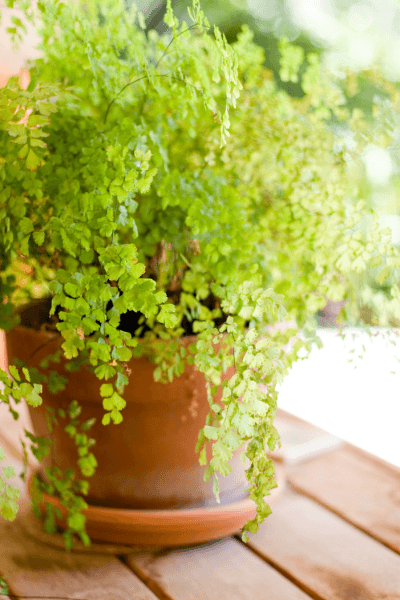
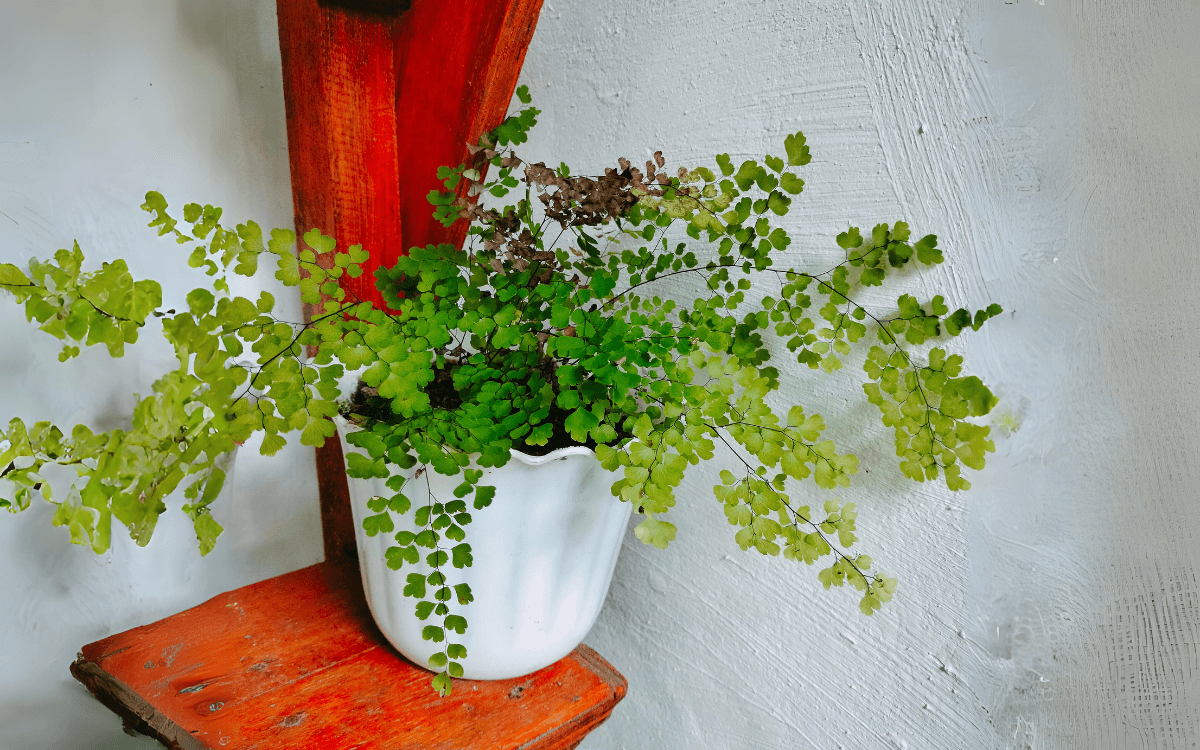Maidenhair ferns belong to the genus Adiantum, they are plants that stand out for their eye-catching leaves and their ability to purify the air.
In this article, I will introduce you to the main characteristics, curiosities, cultivation tips, and various photos of this plant.
Plant Characteristics
Found in nature on rich and moist soils of shaded areas, maidenhair ferns have delicate green-grayish leaves and a highly branched structure.
In addition to their beauty, maidenhair ferns have a history of medicinal use, with their fresh and dried parts being used in natural medicine to combat respiratory diseases and throat ailments, among other therapeutic and nutritional benefits.
Teas made from their leaves are used to treat problems such as hair loss, cough, and throat irritation. However, it is crucial to consult a health professional before using the plant for medicinal purposes and to be sure of its effectiveness.
Maidenhair ferns are part of the Pteridaceae family, which consists of more than 1150 species distributed around the world, especially in tropical regions.
See below the step by step to take care of your maidenhair fern.
Where to Place This Plant
Maidenhair ferns are plants that appreciate indirect light and partial shade.
This means that the ideal place for your maidenhair fern should receive filtered sunlight, avoiding direct exposure that can damage its sensitive leaves.
Positioning the plant near a window covered by a thin curtain can offer the ideal amount of light. This setup mimics the light conditions found in their natural habitats, under the canopy of trees in tropical and subtropical forests.
Additionally, consider placing your maidenhair fern in hanging pots or in vertical gardens.
In planters or arrangements, maidenhair ferns can stand out as central elements, bringing life and color to living or working areas.
Temperature and Lighting
Maidenhair ferns thrive in warm climates, with an ideal temperature range between 13°C (55.4°F) and 30°C (86°F), preferably staying between 18°C (64.4°F) and 25°C (77°F).
Although they can briefly resist colder temperatures, it is essential to ensure that the environment is predominantly warm and welcoming to avoid plant stress.
Another important care is with the lighting of this plant.
Maidenhair fern requires indirect light to thrive. Direct sun exposure can be harmful, burning its delicate leaves. Positioning them in places that receive filtered light, such as near windows with curtains, or in partial shade, is ideal.
Read too:
- Ribbon Fern or Cretan Brake Fern: How to Plant and Care
- Japanese Fern Tree – How to Care and Characteristics
- How to Care for Ferns in 9 Steps (For Beginners)
- Leatherleaf fern – Care, Characteristics and Curiosities
Humidity and Ventilation
High humidity is vital for the well-being of the maidenhair fern, replicating the atmosphere of its original moist habitats
Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, to prevent root diseases.
The use of humidifiers can help you increase the air humidity around the plant, thus ensuring the ideal humidity conditions, which should be around 60%.
While the maidenhair fern benefits from a humid environment, adequate air circulation is essential to prevent diseases, such as the development of fungi.
However, it is important to protect the plant from strong winds or cold drafts, which can damage its thin and delicate leaves and stems. Moderate ventilation helps create a healthy balance, allowing the plant to breathe without being exposed to adverse conditions.
Ideal Soil
The ideal substrate for maidenhair ferns should be rich in organic matter and capable of retaining the necessary moisture without becoming waterlogged.
A well-drained mix, incorporating sand and perlite, is essential to ensure adequate soil aeration and prevent water accumulation, which could lead to root diseases.
The addition of peat to the soil improves moisture retention while maintaining the lightness and porosity necessary for healthy root development.
Soil pH is another crucial aspect for the cultivation of maidenhair ferns. A slightly acidic pH, between 5.5 and 7.0, is most beneficial for these plants, creating a conducive environment for nutrient absorption.
Furthermore, the use of pots with a good drainage layer at the bottom, composed of stones or expanded clay, ensures that excess water can be effectively removed from the roots, preventing waterlogging.
Watering
Regular watering is crucial, with an approximate frequency of three times a week, adjusting as per the climatic conditions.
In hot and dry regions, maidenhair ferns may require more frequent watering, while in cooler climates, the demand for water may decrease.
It is essential to monitor the soil and adjust the watering frequency to ensure that the soil remains moist, but not waterlogged.
Watering Method
Direct spraying on the leaves is the recommended method for watering maidenhair ferns, mimicking the humidity found in their natural habitats.
This should be done carefully to avoid water accumulation on the leaves and stems, which can favor the emergence of diseases.
Watering in the early morning or late afternoon avoids leaving the leaves wet under strong sun, reducing the risk of sunburn.
Below are some additional tips:
- Environmental conditions, such as high temperature, dry indoor environments, and ventilation, can influence the maidenhair fern’s need for water.
- If the stems start to dry out or if the leaves become unsightly, slightly increasing the watering frequency can stimulate the growth of new leaves.
- Ensuring that the pot has good drainage and avoiding leaving water accumulated in the saucers under the pots are recommended practices to prevent excess moisture.
Fertilization
The ideal fertilization for maidenhair ferns involves the use of liquid fertilizers, which should be carefully diluted in the watering water, following the dosage recommendations provided by the manufacturer.
During the active growth period, which typically extends from spring to summer, fertilization should be performed approximately once a month.
This regularity ensures that maidenhair ferns receive the necessary nutrients for their development without being exposed to the risk of overdosing, which can result in leaf burn and premature drop.
During winter, maidenhair ferns enter a period of dormancy, a time when fertilization should be halted.
This rest allows the plants to prepare for the next growth cycle, ensuring they resume stronger and healthier in the spring.
Fertilizer Application
Overdosing can be as harmful as a lack of nutrients, leading to problems such as burned leaves or drop.
The plant absorbs nutrients according to its needs, and excess can accumulate in the soil, negatively affecting the health of the maidenhair fern.
After applying the fertilizer, it is important to water the plant well to help distribute the nutrients through the soil, ensuring they reach the roots and are effectively absorbed.
The correct dilution of fertilizer in watering water is crucial to avoid the accumulation of salts that can be harmful to the plant.
Read too:
- Monarch Fern – How to Care and Propagate
- Marisa Fern: 7-Step Growing and Care Guide
- Rabbit’s Foot Fern (Davallia fejeensis): Cultivation Guide
- Nephrolepis exaltata (Boston Fern): How to Grow and Care
Pruning
Pruning is essential to maintain the health and aesthetics of maidenhair ferns.
Pruning should be performed to remove dry or damaged leaves, which encourages growth and keeps the plant looking vibrant.
Always use clean and sharp cutting tools.
Removal should be limited to dead or diseased leaves, preserving healthy leaves that are crucial for photosynthesis and plant development.
Replanting
Replanting maidenhair ferns is rarely necessary, but when done, it should be chosen an appropriate period, usually after the resting period in autumn.
During replanting, it is vital to keep the roots intact and carefully transfer the plant to a new pot, which should be clean and filled with the appropriate substrate.
Adding a new layer of fresh soil at the bottom of the pot can stimulate new growth and give the plant the necessary nutrients for development.
Propagation
The propagation of maidenhair ferns is a process that can be performed in two main ways:
- Division of clumps
- Germination of spores.
Both methods require specific attention and care to ensure success in propagating these plants.
Division of Clumps
Propagation by division of clumps is a relatively simple and quick method. This process involves the physical separation of an adult plant into several smaller plants, each with its own root system. Here are the basic steps:
- Select a healthy plant and carefully remove it from the pot, trying to preserve as many roots as possible.
- Separate the clump into smaller sections, each with several leaves and a portion of the root system. Ensure each new plant has enough roots to support its growth.
- Plant each section in its own pot, using a suitable substrate that offers good drainage and is rich in organic matter.
Germination of Spores
Germination of spores is a more time-consuming and laborious method. Here are the steps:
- Collect mature spores, which appear as a fine black dust under the leaves of healthy adult plants.
- Spread the spores over the surface of a suitable moist substrate, kept in a germination tray or similar. The substrate should be kept constantly moist.
- Cover the tray with a lid or clear plastic to maintain moisture and place it in a location with light shading and controlled temperature. The germination of spores can take several weeks to months.
- Once the seedlings reach a suitable size for handling, they can be carefully transplanted into individual pots, following the same planting recommendations for adult maidenhair ferns.
Pests
Maidenhair ferns can be susceptible to pest attacks such as mealybugs, mites, aphids, and slugs.
These insects feed on the plant’s sap, harming its growth and vigor.
To prevent infestations, cultivate your maidenhair ferns well and avoid conditions that favor moisture stagnation. In case of infestation, the careful application of specific insecticides, as per the manufacturer’s guidance, may be necessary.
Home remedies, such as neutral soap diluted in water, can also be effective for controlling some pests.
Diseases
Diseases such as bacterial spot and root rot, caused by fungi, are common problems that affect maidenhair ferns.
Prevention involves ensuring a good drainage system and avoiding injuries to the roots during replanting.
Excessive moisture is a risk factor for the development of these diseases; therefore, it is crucial to maintain the ideal moisture balance.
Upon the emergence of symptoms, the removal of the affected parts and the application of specific fungicides may be necessary.
Did you like this text? Then leave a comment below and share it on your social networks.