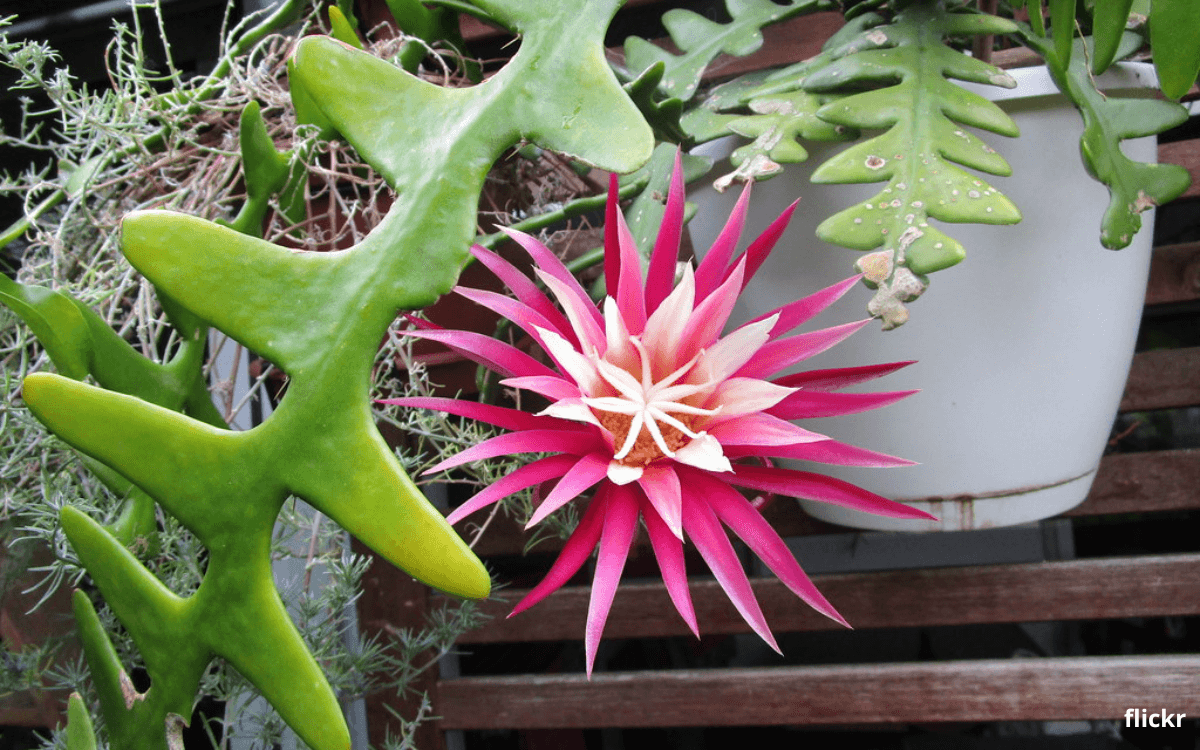
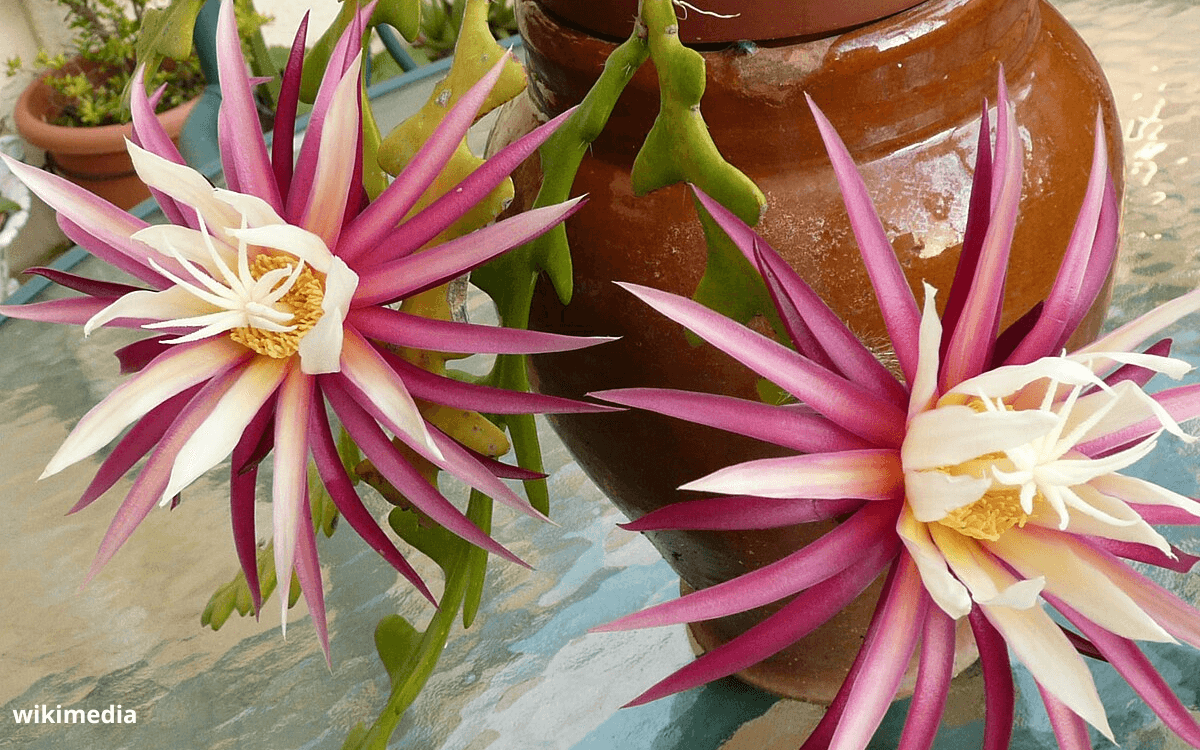
Today, we are going to talk about Selenicereus anthonyanus, commonly known as the fishbone cactus.
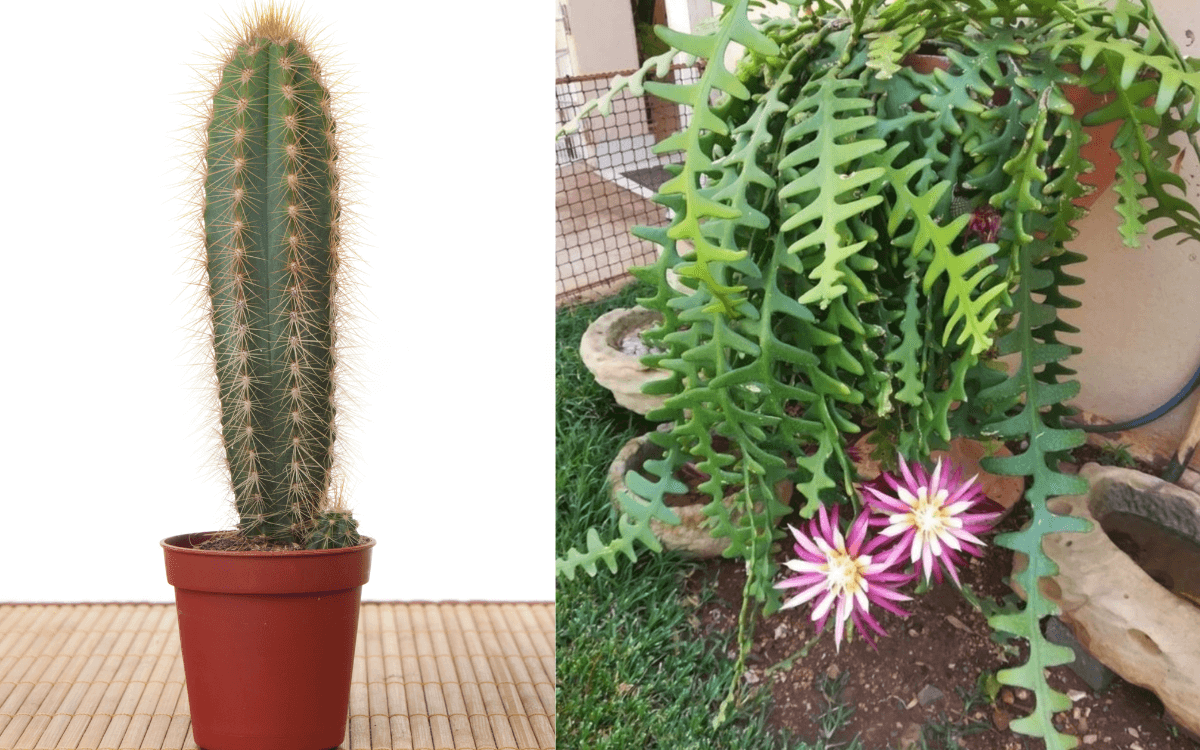
Originating from the warm lands of southern Mexico, this cactus species stands out from the standard cactus stereotype (see image below).
Keep reading because in this article, you will learn more about the characteristics, curiosities, and how to take care of this cactus.
Plant Characteristics – Selenicereus anthonyanus
The Fishbone Cactus has nearly flat stems of vibrant and radiant green, extending up to 1.5 meters (approximately 59 inches).
It can grow in unusual places such as rocks and tree trunks; this Cactus is an epiphytic species, making it a perfect choice for vertical gardens. It can trail like a hanging plant or climb on supports.
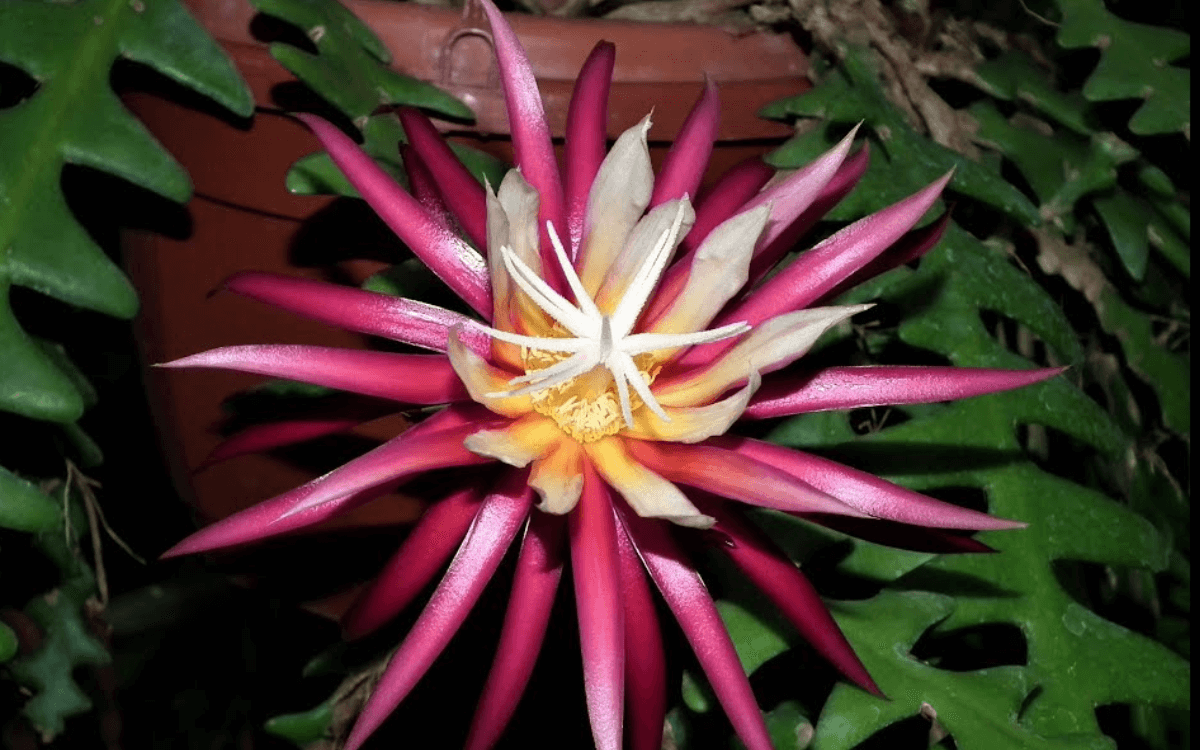
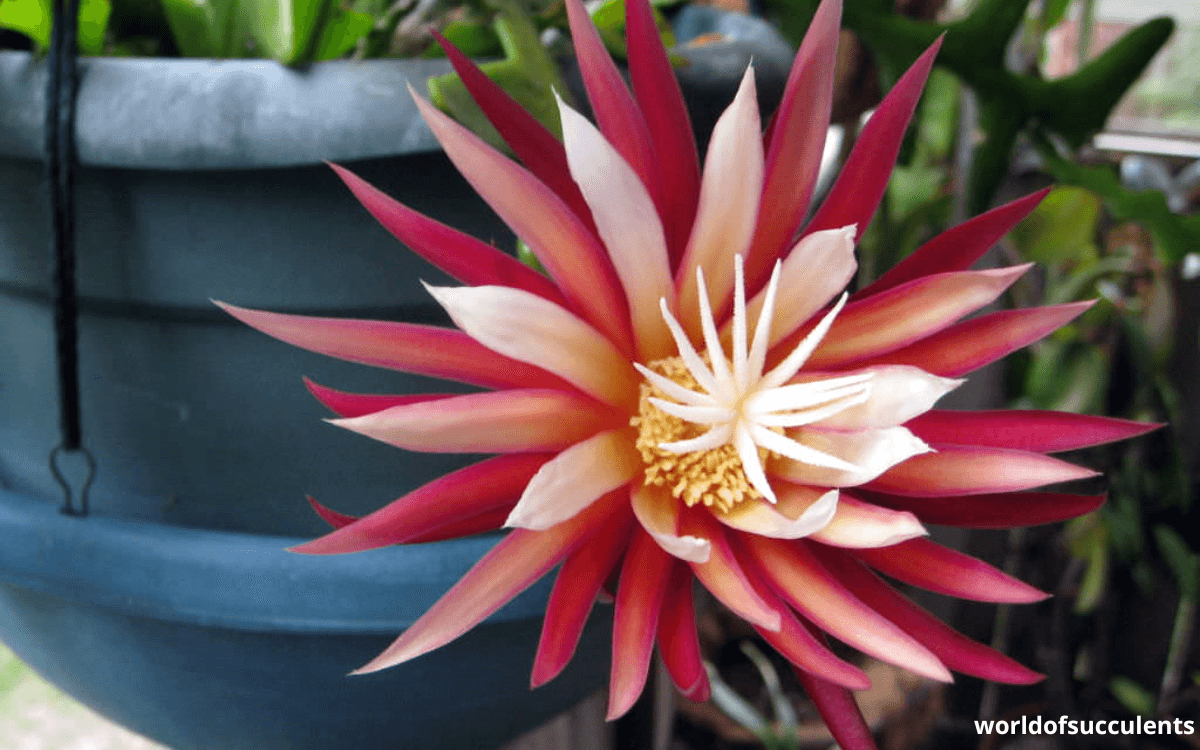
Its nickname in Portuguese “Queen of the Night” is well-deserved because this plant offers a spectacle of nocturnal flowering during the spring and summer. Its flowers unfold in layers of pink and cream, with a diameter that can reach 15 to 17 centimeters (approximately 6 to 7 inches).
The Fishbone Cactus thrives in a wide range of environments, from arid soils to the dampest conditions of savannas and tropical forests, demonstrating its remarkable adaptability.
While some cultures use the Selenicereus anthonyanus in medicinal and cosmetic preparations, it is advisable to approach such practices with caution due to the scarcity of scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness.
Facing threats in its natural habitat due to human intervention and climate change, the conservation of the Fishbone Cactus is of utmost importance, emphasizing the urgent need to protect and preserve this wonderful species for future generations.
Read more about cactus:
- Monkey Tail Cactus: How to Care and Propagate
- How to Care for Cactus and Mini Cactus (7 Simple Steps)
Curiosities and Interesting Facts About the Fishbone Cactus
The nomenclature ‘Selenicereus‘ is a tribute to Selene, the Greek goddess of the moon, a poetic choice that reflects the majestic nocturnal blooming of this cactus.
The addition of ‘cereus‘, Latin for ‘candle‘, suggests an allusion to the elongated and luminous flowers that resemble candles glowing in the dark.
The epithet ‘anthonyanus‘ honors Harold E. Anthony, a naturalist who played a crucial role in the discovery and recognition of this plant in the mid-20th century.
The Selenicereus anthonyanus is native to the southern regions of Mexico, where it intertwines in tropical forests and savannas. Despite this, this plant can adapt to a diverse range of environmental conditions, from dry and sandy soils to the wettest ones.
The beauty of the Fishbone Cactus comes with a note of caution, especially for pet owners, due to its toxicity.
Be aware of this characteristic when deciding on the ideal location for this plant in your home or garden.
Where to Plant
Known for its resilience and showy flowers, this cactus can be grown in various environments, from outdoor gardens to indoor spaces, as long as its specific needs are met.
Below, we will detail the ideal conditions and the most suitable locations for cultivating this stunning plant, ensuring that it not only survives but also thrives and blossoms.
Choosing the Ideal Location
The first step in choosing the ideal location for your Fishbone Cactus is to ensure that it has enough space to grow both vertically and horizontally, especially if it is planted in pots or alongside other plants.
Taking advantage of its epiphytic nature, consider planting it on tree trunks, rocks, or structures that allow its aerial roots to develop freely, creating a naturally stunning look.
For indoor environments or balconies, opt for pots with good drainage.
Pots allow you to control soil conditions and make it easier to move the plant if needed to adjust light exposure.
If you have pets, choose a location where they do not have access to the plant, avoiding health risks due to the plant’s toxicity.
Ideal Climate
Native to tropical regions, the Fishbone Cactus is accustomed to warm climates and has remarkable tolerance for dry periods.
This adaptability allows it to thrive in various climate conditions, as long as extreme temperatures are avoided.
It prefers moderate lighting, with a combination of direct sunlight and partial shade. The ideal temperatures for its growth are between 77°F and 95°F during the day, not dropping below 59°F at night. This preference for warmer daytime temperatures and cooler nights reflects its natural habitat.
Although it tolerates drought well, environments with good air circulation and controlled humidity are ideal, avoiding the risk of fungal diseases and root problems.
Adequate ventilation is crucial to maintain the ideal moisture balance around the plant.
Ideal Soil
The soil should be well-drained, nutrient-rich, with a mixture that promotes rapid water drainage. You can use:
- Sand
- Perlite
- Gravel
- Another option is to use a mixture of sand, gravel, and peat.
Adding organic matter, such as peat or compost, to the soil not only enriches it with essential nutrients but also helps maintain the ideal soil structure for root growth.
The ideal soil pH for the Fishbone Cactus should range from 6 to 7, a balance that can be achieved by adjusting the soil composition with additives like lime, if necessary.
Watering
Watering should be moderate, adjusting to the weather conditions and the cultivation environment.
During the warmer months or in drier climates, weekly watering may be necessary, while in colder or cloudy periods, reduce the frequency to avoid excess moisture.
It is essential to ensure that the soil has excellent drainage to prevent water accumulation.
Overwatering the soil can lead to root rot, an adverse condition that can be fatal for the plant.
Below are some additional watering tips that can help:
- Always use room-temperature water to water the fishbone cactus. Water that is too cold or too hot can shock the plant’s sensitive roots and affect its development.
- The roots of this cactus can benefit from occasional misting. This helps maintain the ideal moisture, especially in drier environments or during the warmer months.
- Keeping the soil consistently moist but not saturated is vital. The soil should allow the roots to breathe without becoming waterlogged, balancing the need for moisture with protection against root rot.
Ideal Fertilization for the Fishbone Cactus (Selenicereus anthonyanus)
To fertilize your plant, you can use organic or chemical fertilizers or apply both, being careful not to overdo the fertilization.
Remember to apply the fertilizer to the soil, avoiding direct contact with the plant to prevent chemical burns on the roots or base of the cactus.
- Use of Organic Fertilizers: In spring and summer, during the active growth periods of the cactus, apply organic fertilizers that release nutrients gradually. This can include compounds like worm castings or well-rotted and sterilized manure, which not only nourish but also improve soil structure.
- Use of Chemical Fertilizers: Another option is specialized cactus fertilizers with a 04-14-08 formulation (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium), which promote an ideal balance for growth and flowering. This type of fertilizer also provides essential micronutrients that support overall plant health.
When fertilizing the Fishbone Cactus, it is crucial to follow the instructions specified on the fertilizer packaging, adjusting the dosage and frequency of application as needed. This will prevent the risk of overfertilization, which can lead to root burns and harm the plant.
Limited fertilization to periods of active growth, usually in spring and summer, reducing or eliminating fertilization during the autumn and winter months when the plant enters a dormant period.
Dealing with Pests, Diseases, and Common Problems
Mealybugs and Spider Mites: These pests are attracted to low humidity conditions. Manual removal or the use of specific insecticides can be effective. For mild infestations, homemade solutions like a water and alcohol mixture can help.
Excessive Water: Watering should be careful to avoid soil saturation. Good drainage is essential to prevent root rot, one of the most common causes of cactus death.
Black Rot: This serious condition can be prevented with proper watering care and ensuring that cuts or wounds on the plant are treated to prevent infection. The removal of affected parts and treatment with fungicides may be necessary in advanced cases.
Issues with Direct Sun Exposure: The Fishbone Cactus can suffer from sunburn if exposed directly to intense sunlight. Prefer locations with filtered or indirect light to prevent leaf damage.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular inspections will help identify early signs of pests, diseases, or water stress, allowing for quick interventions to resolve problems.
I hope that by following these cultivation tips, you can keep your Selenicereus anthonyanus healthy and ready to produce incredible blooms every year.
Below are some articles about cacti that have been published on this website, and if you enjoyed this text, please share it on your social media.